Pinochle is one of the most fun and challenging card games in the world. Much like Poker, it requires skill in estimating probabilities, strong instincts on when to be cautious or when to take risks, and an ability to read your opponents to gauge the strength or weakness of their hands. However, Pinochle requires deeper analysis and more strategy than Poker. Perhaps one could say Pinochle is to Poker as Chess is Checkers. If you enjoy the mechanics of Poker, but think you’re ready to try something more thought-provoking, Pinochle is definitely worth checking out.
There are many different variations of Pinochle and many players have their own unique rules and preferences for how to play. In this introduction, we’ll start with covering the basics and most universal concepts. We’ll describe some of the most common styles of playing and basic strategies. In subsequent articles, we’ll go into more detailed descriptions of specific versions and elaborate of on how to employ effective strategies for each.
Pinochle Decks
Pinochle is played using a specialized deck of 48 cards consisting of Aces, Tens, Kings, Queens, Jacks, and Nines. There are two of each card for every suit. Unlike a standard 52-card deck, there are no cards between Two through Eight. When playing with physical cards, one can either purchase a special Pinochle deck or use two standard 52-card decks and remove all of the numbered cards below Nine.
In Pinochle, Aces are the highest card, followed by Tens, then Kings, Queens, Jacks, and Nines.
Some players prefer to play double-deck Pinochle, which means two decks are used instead of one. However, most players will remove Nines when playing double deck, leaving a total of 80 cards.
Number of Players
Most variations of Pinochle require either 3 or 4 players (there are 2 player versions and versions with more than 4 players but these are less common). 3-player or 3-handed Pinochle is often referred to as Cutthroat because it requires each player to play against the other two (i.e. every man or women for themselves). However, in most 4-player variations, partners are chosen and two players form a team to compete against the others.
Dealing
Normally, a random player is selected to be first dealer and then for each subsequent hand the player to the dealer’s left deals the next hand. At the start of each hand, the dealer shuffles the deck and begins dealing all cards face-down, starting with the player to their left, and then around the table clockwise, dealing to themselves last. In single-deck Pinochle, the dealer typically deals 3 cards to each player at a time, whereas in double-deck it’s usually 5 cards at a time. If there are four players, in most variations, cards are dealt evenly to each player until there are no cards left in the deck: 12 cards to each player if single deck or 20 cards to each player if double deck. However, in Cutthroat, often the last set of cards (3 cards in single-deck, or 5 cards in double deck) are placed face-down on the table into the “kitty”, which will be used later in the game.
Bidding
Most variations of Pinochle involve a bidding phase in which players wager on how many points they believe they can earn by the end of the hand. The highest bidder gets honor of choosing the Trump suit, and often gets to either pass cards with their partner or take cards from the kitty to form a better hand. However, if a player over-bids and fails to make their bid amount by the end of the hand, they will be penalized by losing the amount of points wagered and forfeiting any points earned in that hand.
After all cards are dealt, players pick up their hand and must evaluate how many points they think they might earn. There is usually a minimum starting bid and a set bidding increment that all players agree to before the game begins. The player to the left of the dealer is the first to place a bid or may choose to pass. The bidding goes around clockwise, and each player must decide to either raise the bid by the bidding increment or pass. When all but one players pass, the remaining player wins the bidding.
Taking Cards from the “Kitty”
Often in Cutthroat Pinochle, and in some variations of Partner Pinochle, the Kitty is used to give the high bidder an opportunity to strengthen their hand. The high bidder gets to pick up the cards in the kiddy and decide if they want to trade them with cards in their existing hand, discarding the cards they don’t want to use.
Choosing the Trump Suit
The winning bidder gets to decide which of the four suits will be the trump suit during the hand. The trump suit is significant both in calculating meld points and in the trick-taking phase of the game. As described more below, certain melds require cards to be of the trump suit, and others are worth more points when they are in the trump suit. When it comes to trick taking, a card in the trump suit will “trump” all non-trump cards and win the trick, therefore having a lot of trump cards gives the player a significant advantage when competing for trick points.
The high bidder must carefully evaluate their hand and choose the trump that will be most advantageous. Having a lot of cards in one particular suit often would suggest choosing that suit to be trump, but the player must take into account expected meld points, their trick-taking approach and if playing with a partner consider what additional cards might be received after passing.
Partner Card Passing
Often in Partners Pinochle, after the high bidder chooses the trump suit, they have an opportunity to improve their hand by exchanging cards with their partner. Partners are not allowed to show their cards to each other or tell their partners directly what cards they’re holding, but in some styles of play partners communicate with their bids, for example a player who makes an opening bid of 25 may be signaling they have Aces Around, or an opening bid of 30 may signal they have a run, or an opening bid of 35 may signal they have double pinochle. Typically the partner of the high bidder passes first, passing 4 cards to the high bidder. Next the high bidder evaluates their cards and chooses 4 card to pass back.
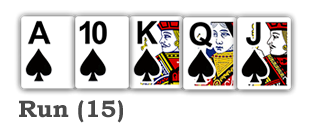
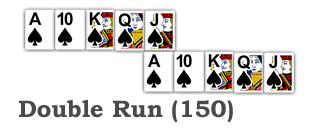
Pinochle Melds
Most variations of Pinochle include a melding phase, in which players earn points by completing special sets of cards known as melds. Each type of meld is worth a set number of points as shown below, and players receive the total points for all of the melds in their hand. When playing with a partner, each player forms their own melds based on the cards in their own hand, and then the point totals from each are added together. For example, if Player A has a run worth 15 points, and a marriage worth 2 points, their total melds is worth 17 points. If their partner, Player B has a Pinochle worth 4 points and a trump 9 worth 1 point, Player B’s meld total would be 5 points. Player A and Player B’s meld point totals are then added together for a combined meld score of 22 points.












Pinochle Trick Taking
The final phase of the Pinochle hand is the trick-taking phase. The high bidder goes first by throwing down any one of their cards face up in the center of the table, and then each of the others must throw a card after that in a clockwise rotation. Each subsequent player following the trick starter must throw down a card of the same suit as the first card thrown if they have one. If they don’t have any cards in that suit, they must throw a trump card, unless they don’t have a trump card either, and only then they can throw any card they want.
The highest card matching the suit of the first card thrown wins, unless someone throws a trump card in which case the highest trump card wins. If there’s a tie, meaning two players both throw the same highest card, then the player who threw the high card first wins the tie. The player who wins the trick takes the trick cards and gets 1 point for every Ace, Ten or King. These three cards are called pointers because they’re each worth one point. Queens, Jacks, and Nine’s have no trick value.
The winner of the trick then becomes the trick starter of the next trick, and the trick taking continues until all cards are played. At the end of the trick taking phase each player tallies their pointer cards and their trick points are then combined with their meld points. If the high bidder meets or exceeds their bid they get to keep all meld and trick points earned in the hand. In Partner Pinochle, the high bidder and their partner combine these points to reach their goal. However, if the high bidder comes up short they will not keep any of the points earned in the hand and instead must subtract the amount they bid from their score. The opponents of the high bidder get to keep their points regardless.
Ending the Game
Most variations of Pinochle end when a certain predetermined score is reached such as 150 points. The first player or pair of partners who earn this score wins. In the meantime, the players continue to deal hands and repeat the process described above, earning (or losing) points in each hand and adding them to their final score until winning threshold is reached.
At a high level, this is how Pinochle works. There are many nuances and strategies that expert players develop over time, some of which will be discussed in future articles on this site, but we hope this primer will give you the basics you’ll need to get started. These rules may seem a bit complicated at first but the easiest way to master them is to just start playing. We recommend trying a few games with our AI Pinochle to get a feel for how the game works and then once you feel confident try playing online with real players. We rank players on this site based on their experience so you’ll be paired with other players at the same level as you.
We hope this tutorial was helpful and look forward to seeing you at our tables soon.